Suggested indicators
After analyses of existing monitoring frameworks, stakeholders from the Urban Agenda Partnership assessed the long list of indicators from the existing models according to the following criteria: „Core/additional indicator (2 = core; 1 = additional, 0 = not...
Existing indicator frameworks
The publication from the Urban Agenda partnership also offers an overview of existing frameworks for monitoring the circular transformation. Some of the most prominent ones are listed in the table below. PublisherReport / projectFocus / special featureECIn-depth...
Objectives of CE indicators
„In order to develop and implement a CE strategy in urban environments it is crucial to find a framework of indicators to monitor the progress and performance and, when necessary, adapt the ongoing processes. Based on the literature review, the following objectives of...
More information
EU EU waste policy aims to contribute to the circular economy by extracting high-quality resources from waste as much as possible. The Waste Framework Directive (2008) is the EU’s legal framework for treating and managing waste in the EU. It...
References
Circular Cities Declaration (2020), Key Circular Economy sectors, [online] https://circularcitiesdeclaration.eu/cities-and-the-circular-economy/key-sectors(accessed: 2021/12/28)European Commission (2015), Waste,...
Examples of innovative solutions
An innovative example, how a smart city could improve the waste management can be found in the city Nitra in Slovakia. In 2015 the company “SENSONEO” started to equip public garbage collection bins with sensors that are able to measure the filling level of the...
Technological factors
There are plenty of technologies and innovations that are able to improve the waste management of a city and make it more sustainable. The fields of application for those technologies vary. The most common technologies that are supporting the waste management are high...
Social and cultural factors
Even if waste is not the most social topic, there are still a few administrative things to be aware of when it comes to waste management. How already mentioned, in the environmental section, the reduction of waste is the most effective way to prevent environmentally...
Legal and political factors
There are many regulations and agreements on the European level that are aiming at the reduction of generated waste and the increase of reusing waste. The European green deal for example, provides guidelines how to reduce and how to reuse the waste. The main...
Environmental factors / ecological footprint
The different problems are explained more in detail in this section (European Environment Agency (2014)): Air emissions: If the waste of a city is not managed in a sustainable way, much of it will be disposed in landfills or burned in waste treatment facilities....
More information
EU and other websites EU _ Mobility and TransportEltis _ The Urban Mobility Observatory “Eltis facilitates the exchange of information, knowledge and experience in the field of sustainable urban mobility in Europe.” CIVITAS initiative _ Sustainable and smart...
References
[1] Padam Mobility. (2021). Urban mobility: the new forms of transport. [online]. Available at: https://padam-mobility.com/en/the-new-forms-of-urban-mobility/ [Accessed 1 Jan. 2022]. [2] Mobilität in Deutschland –...
Example of innovative solutions
In the following part some innovative solutions for a more sustainable and better service system in the field of mobility and transport in a city are presented. Circular support models Urban transport is responsible for almost half of urban energy consumption and 90%...
Technological Factors
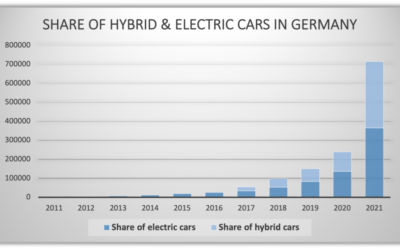
A major technological factor for the mobility sector is the advancing electric mobility. These offer many advantages: Electromobility enables emission-free drivingDue to the high energy efficiency of electric cars, they enable drastic energy savings in...
Social & Cultural Factors
Social and cultural factors strongly influence mobility. The growth rate of cars within a city is crucial for air pollution and the overall ecological footprint. Social factors such as trends that arrive in the environment are also a big...
Legal & Political Factors
The European Green Deal (COM(2019)640) and the Sustainable and Smart Mobility Strategy (COM(2020)789), adopted in 2019 and 2020 respectively, provide a new EU framework for the overall direction of EU transport policy for the years to come, and...
Environmental Factors / Ecological Footprint
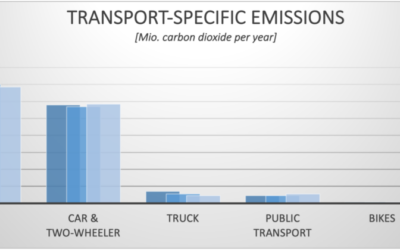
Mobility and traffic on the roads cause considerable ecological, social, and economic damage and burdens. The share of traffic in air pollutant emissions is more than 50 percent for carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides. The high and increasing carbon dioxide...
More information
EU and other websites EU _ Energy: website Policy briefs Championing sustainable energy in SMEs: Jun 2021; Interreg Europe _ PLPSkills for the Energy Transition: Feb 2021; Interreg Europe _ PLP Supporting local bioenergy development: Mar 2020; Interreg Europe _...
More information
EU and other websites European Commission_ Evaluation of the impact of the CAP on water: 2020European Commission _ Horizon 2020 Water Innovations for sustainable impacts in industries and utilities: 2020European Environmental Agency _ Water and marine...
References
Biodiversitätsstrategie für 2030. Environment. (n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2022, from https://ec.europa.eu/environment/strategy/biodiversity-strategy-2030_de Chemicals strategy. Environment. (n.d.). Retrieved January 19, 2022, from...
Examples of innovative solutions (good practices)
Portugal Portugal created a national action plan with 7 key objectives. design, repair, and reuseincentivizing a circular marketeducating for a circular economyeating without wastinggiving waste a “new life”regenerating water and nutrientinnovating for a circular...
Technological factors
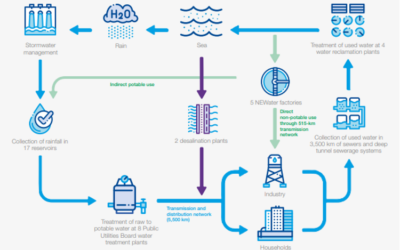
It’s most important to close the circle of water usage and reduce wasted water, this circular use of water has to include all waters and materials in the water, to effectively be more sustainable. This closing of the water loop must have the goal to reduce wastewater...
Social and cultural factors
As stated, human pollution effects water resource, but also the general effect of a growing population puts a strain on water resources. As it is expected the world population will grow over 7 billon people in next years a problem becomes apparent. This rising...
Legal and political factors (only European level)
The European union declared on of their goals of the green deal is to create more clean water and a restoration of biotopes, to increase a more health life for all. [4] One of these strategies is the biodiversity plan for 2030, which has the overall goal to protect...
Environmental factors / ecological footprint
Manmade extreme weather phenomena will increase in the next years which will strain water supply. As there will be longer and more often occurring droughts in one area, but also more flooding in other areas. Which will make water availability more unpredictable...
More information
EU EU _ EnergyEU _ Energy _ Energy efficiencyEU _ Energy _ Energy efficiency – Energy efficient buildingsEU _ Energy _ Energy efficiency – Energy efficient buildings Energy performance of buildings directive “The building sector is crucial for achieving the EU's...
REFERENCES
[1] Leonora Charlotte Malabi Eberhardt, Morten Birkved & Harpa Birgisdottir (2020) Building design and construction strategies for a circular economy, Architectural Engineering and Design Management, DOI: 10.1080/17452007.2020.1781588...
Technological factors
To transform buildings and the construction process in sustainable and circular way, different technologies can be applied. Smart Buildings Trough the implementation of electrical devices like sensor and the connection between them, smart buildings will help to...
Social and cultural factors
The increasing growth rate of the world’s population paired with the concentration on big cities requires a rapid solution for green, sustainable, and affordable housing. In addition to the rising awareness about climate change issues, a circular approach can...
Legal and political factors (only European level)
Due to the significant impact of buildings and the construction industry on the economy, jobs and quality of life, the EU addresses this issue in its “Circular Economy Action Plan”. By considering the safety and functionality of construction products, the EU plans to...
Environmental factors / ecological footprint
The construction of building and respectively the building sector word wide causes about 39% of the man-made emissions. About a quarter of this emission (≈11%) comes from the production of building materials. In addition, about 50% of the global material...
References
Fusco Girard, L., & Nocca, F. (2019). Moving Towards the Circular Economy/City Model: Which Tools for Operationalizing This Model? Sustainability, 11(22), 36–48. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226253 Geray, O. (2020). A guide to circular cities....
Examples of innovative solutions (good practices)
Urbanscapes Group organized the symposium with the main objective of bringing together experts, practitioners and users from different countries and backgrounds to review and discuss existing tools and approaches in implementing good public urban spaces, and to...
Technological factors
The smart digital networking of public spaces has help improve not just the space and quality, but statements about the city dwellers should be possible to make thanks to the collection of dynamic data. Constant evaluation can be used as a basis for the development of...
Social and cultural factors
For economic expansion, investment is an important aspect which depends on mobility, safety and attractiveness, this together makes the cycle of public space. Public spaces provide important benefits to businesses in formal and informal ways. Another...
Legal and political factors (only European level)
The European Green Deal makes the concept of circular economy the centre of efforts to transform the European Union into a fair and prosperous society, where economic growth is decoupled from resource use and environmental harm. In light of the socio-economic impact...
Environmental factors / ecological footprint
For the past years, global warming has been a major problem in the world, therefore it has been foreseen that to be able to limit it to 1.5º, it is important to reduce the emissions generated by 7.6% every year from 2020 to 2030. As the European Union has remarked,...
More information
Introduction EU Ecosystem services and Green Infrastructure: website EU Further links to key references are given, e.g.: The EU Strategy on Green Infrastructure: website EUGreen infrastructure in policy: website EU Further links to information are given, e.g.:...
More information
Papers / books M. Randelhoff, „zukunft-mobiliteat,“ 28 Dezember 2017. [Online]. D. B. Hendricks, „bmi.bund.de,“ 2015. [Online]. Urban land use planning as an enabler of economic growth: 2020; Collier, P., Glaeser, E., Venables, A., Manwaring, P.; IGC Cities that Work...
Good practice
HLJ2015- Integrated planning process of land use plan, housing strategy and transport system plan: Mar 2018; Good practice _ project SMART-MR (see also 1.3.2.3 Mobility / transport)
Examples of innovative solutions
Planted buildings: New ideas shows buildings with grasses or small trees on it. On the balcony for example or the roof. Furthermore, this innovation helps to optimize the land use of an urban. During the building of a building the environmental trees and grasses...
Technological factors
Technologies will and are playing an important role for cities and the inhabitants on fighting against the climate change and to become more “greener”. Several technologies have already been developed which are exactly invented for this purpose. Two technologies...
Social and cultural factors
The population is getting older and older. Moreover, the birthrate goes down, but don’t affect the increasing population. Couples and families have different backgrounds. As a result, cultures are mixing. This shows us that the living situation and need have changed....
Legal and political factors
The purpose of the Green Deal is to make a better and healthier life for the people and future, through building energy-efficient buildings and public transports. The reason is, that most of these produce CO2. For buildings it is the used materials like cement and for...
Environmental factor/ ecological footprint
Environmental factors affect the health and well-being of urban residents. Throughout the land use history, forests are deforested to build buildings. This affects the environment and plays an active role in climate change. Because the trees absorb and store the...
The importance of land use
Land is the most valuable asset in a city. The use and structure of urban land is decisive in determining the potential for individuals to access jobs, services, and collectively drive productive growth. Effective land use: Creates a platform on which firms and...
More information
Definition European CommissionPublic Procurement for a Circular Economy - Good practice and guidance The European Commission published the brochure in Oct 2017 in order to support public purchasers to leverage support for a transition to a circular economy....
Sources for further information
The article Mapping Industrial Symbiosis Development In Europe_ typologies of networks, characteristics, performance and contribution to the Circular Economyprovides an extensive overview of Industrial Symbiosi activities in Europe. It contains among others a...
Projects on Industrial Symbiosis
Interreg Europe SYMBI - Industrial Symbiosis for Regional Sustainable Growth and a Resource Efficient Circular Economy (2016 – 2021) SYMBI aims at supporting the transition towards a resource-efficient economy through industrial symbiosis, establishing...
Industrial symbiosis creates an interconnected network
Industrial symbiosis creates an interconnected network which strives to mimic the functioning of ecological systems, within which energy and materials cycle continually with no waste products produced. This process serves to reduce the environmental footprint of...
Examples of circular recovery models
Bumble Bee Bags give reflective vests a second life (Germany)ECOPLAST FIBER JSC recycles PET bottles into flakes and fibers (Bulgaria)Kunst vom Rand e.V. design various products, e.g. out of fire hoses, old books and can tabs (Austria)LAVU collects...
Examples of optimal use models
Reuse & Repair & Product-life Extension Jausnwrap: Beeswax cloth food wraps as a natural alternative to plastic wrap and aluminium foil for food storage (Austria)Recycle it has, besides an e-waste recycling plant, an online shop for refurbished...
Examples of circular design models
alvari designs and produces customisable furniture from local resources and offers a take-back system to its customers (Germany)GreenLab utilizes cocoa waste material for production organic fertilizer (Germany)TRIGEMA produces biodegradable, Cradle to...
9R Framework
The model suggested by the PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (2017) is presented in the figure below. The model which defines ten strategies for circularity that can be used to build a successful circular product and material flows across the EU. Each...
ReSOLVE framework
The Regenerate – Share – Optimise – Loop – Virtualise – Exchange (ReSOLVE) framework has been developed by McKinsey Center for Business and Environment and u the Ellen McArthur Foundation. Source: Towards a circular economy: Business...
Five business models for circular growth – Accenture
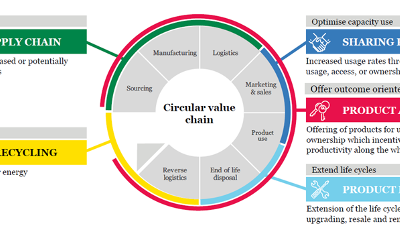
Accenture has developed a model identifying five main business models: Circular Supply Chain (reformed use of resources), Sharing Platform (optimise capacity use), Product as a Service (offer outcome-oriented solutions), Product Life Extension (extend life cycles) and...
Rationale for the circular transition of businesses
As stated in the EIB Circular Economy Guide – Supporting the circular transition, “the shift to a circular economy requires companies to rethink not only their use of resources but also to redesign and adopt new business models based on...
Reducing exposure to ‘linear risks’
Another approach for businesses to the transition towards a circular economy is the reduction of their exposure to “linear risks”, i.e. the exposure to the effects of linear business practices, a concept introduced by Circle Economy, PGGM, KPMG, EBRD, WBCSD,...
Value optimisation principle
Value optimisation is the guiding principle for circular businesses. According to this principle, companies must keep all products, components and materials at their highest value and utility at all times. Value added is in cost-saving, in lower environmental impact,...
More information
Sustainable Development Goals | European Commission (europa.eu) Sustainable development is a core principle of the Treaty on European Union and a priority objective for the Union’s internal and external policies. Overview - Sustainable development indicators -...
More information
A European Green Deal _ Striving to be the first climate-neutral continent (website)Communication and roadmap on the European Green DealThe European Green DealAnnex to The European Green Deal Interreg The European Green Deal: Making Europe the first climate-neutral...
More information
Circular Economy Action Plan (website)Communication and roadmap on the Circular Economic Action PlanA new Circular Economy Action Plan for a cleaner and more competitive Europe Annex to a new Circular Economy Action Plan for a cleaner and more competitive...
More information
Circular Cities Declaration (website)European Circular Cities Declaration (declaration)European Circular Cities Declaration _ Putting Circular Economy into Practice (support document)
Challenges – a selection
How to monitor progress on the CE and macro-level when the baseline is so limited.There is a substantial time lag – when to expect effects and communicate them.Measuring circularity at a city level requires both a city wide CE metrics and a municipality narrative...
Indicator needs
„Through the implementation of a CE approach, cities have experienced the need of indicators for monitoring and to report on their efforts and achievements. The Partnership on CE has identified the lack of such indicators as a bottleneck for cities in implementing a...
More information
LINKS for further information The approach presented in this website builds on the following frameworks and guides for circular cities. For detailed information please follow the links: Based on the key functions of a city that need to become circular, the question is...